VIEW OUR CAUSES
Donate now
BECOME A VOLUNTEER
Join us now
VIEW OUR EVENTS
Get involved
Causes that need your urgent attention
Injustice, inequality, and lack of access to basic resources continue to hold communities back from realizing their true potential. At Debate Lok Nyas, we identify pressing challenges that demand immediate action—be it empowering marginalized groups, improving healthcare and nutrition for children and mothers, or ensuring access to quality education. Your support can make a tangible difference in addressing these urgent issues.
Our Top Stories

Safe City Initiative Madhya Pradesh (2018–2023)
Partnering with UNICEF to support field-based organizations and the Bhopal Municipal Corporation.

Economic Survey of Madhya Pradesh
Contributing to the chapters of development as part of the team drafting the state’s economic survey.

Capacity Building Program in Madhya Pradesh
Collaborating with AIGGPA to build capacities in areas such as monitoring, evaluation and governance.

Developing Tribal Development Plans
Focus: Need assessment and planning for tribal communities in Dhar, Indore, Khargone, Betul, and Chhindwara.
About Us:
Debate Lok Nyas is a dedicated trust committed to empowering communities, fostering participatory governance, and driving sustainable development. With a belief in the power of informed debate and dialogue, we aim to create platforms that amplify voices, inspire action, and bring transformative change to society.
Our Journey:
Founded in the year 2000 as an informal collective of like-minded individuals, Debate Lok Nyas was formally registered as a public trust in 2002. The organization was born out of the need to address critical gaps in grassroots governance, community development, and capacity building.
From its early days of mobilizing local bodies and facilitating participatory planning in rural Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, Debate Lok Nyas has expanded its scope to include policy advocacy, health initiatives, livelihood enhancement, and education programs. Over the years, we have partnered with numerous organizations, including UNDP, UNICEF, Action Aid, and state governments, to design and implement impactful projects that uplift marginalized communities.
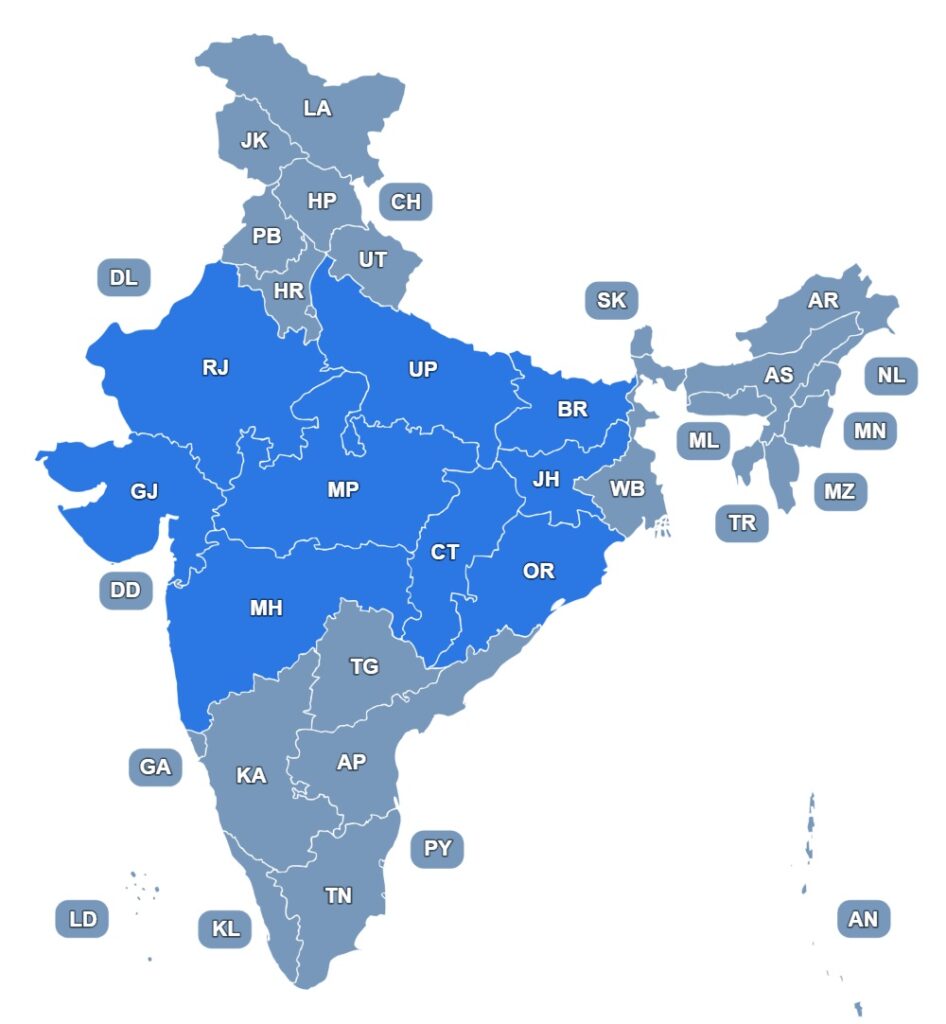
Our Presence
Debate Lok Nyas has established a strong presence across Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, with impactful initiatives spanning rural, urban, and tribal communities. Our expertise and collaborative efforts have extended to other states, including Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra and Gujarat. With over two decades of grassroots involvement, we have worked alongside governments, international agencies, and local organizations to address critical challenges in governance, health, education, livelihoods, and sustainable development. Our widespread presence ensures that we bring localized, inclusive solutions to the forefront, empowering communities and fostering participatory governance at every level.
Let's start doing your bit for the world. Join us as a Volunteer
Our Partners & Colleborators











Some of the success initiatives










Awards and Recognitions












